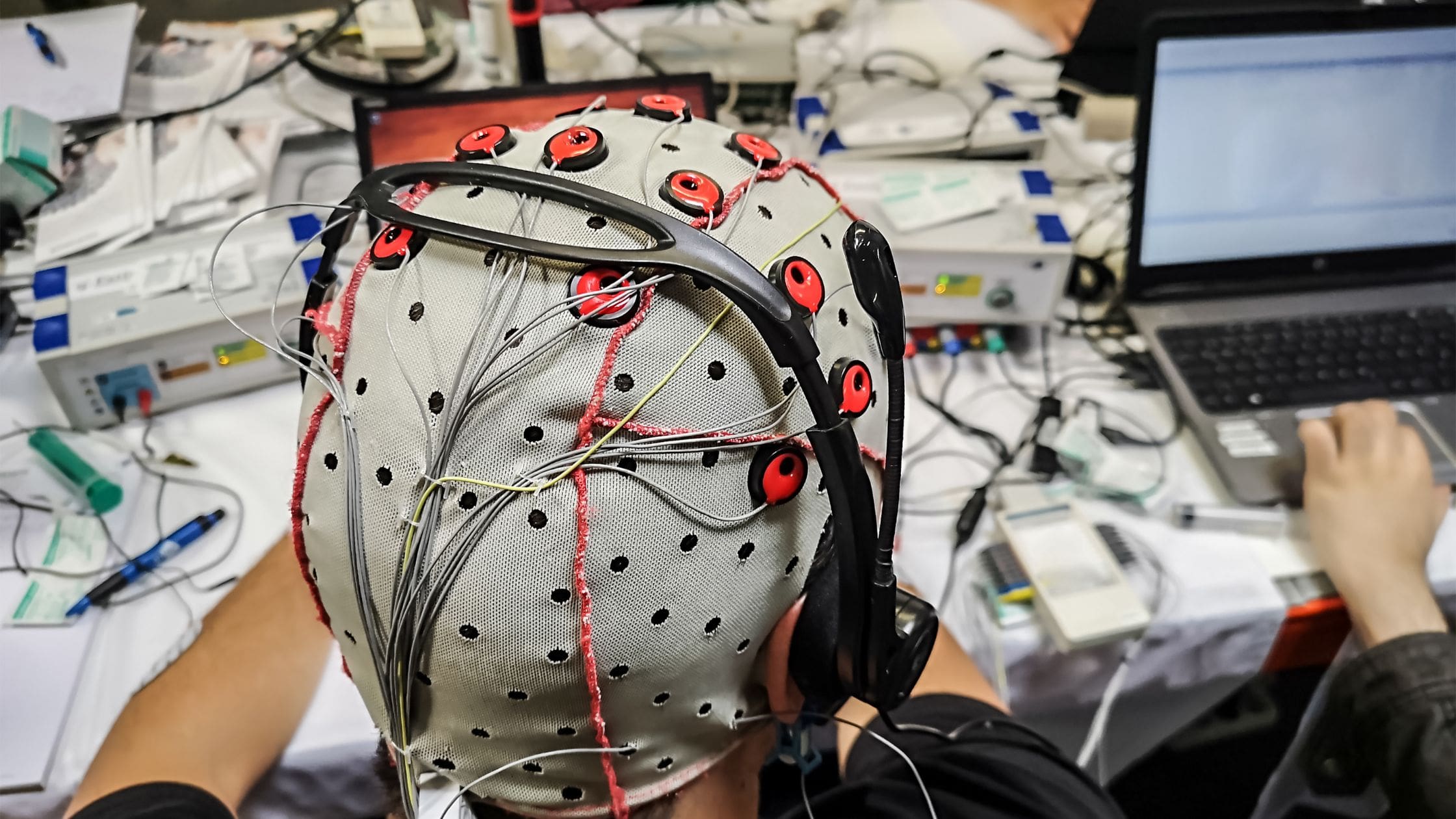
Brain-computer interface (BCI) technology stands at the forefront of scientific innovation, establishing a direct bidirectional communication channel between the human brain and external devices. It interprets brain signals and translates them into commands that control devices, allowing individuals to interact with technology using their thoughts.
The potential applications of these devices span from restoring mobility for individuals with paralysis to enhancing cognitive abilities. While it is still a very new technology and hasn’t been widely adopted or implemented into the mainstream, it’s essential to understand that accessibility and ethics are important to integrating it into everyday life — and perhaps allowing users to take control of the in-brain app in convenient ways.
Innovations in Brain-Computer Interface Technology
Recent advancements in BCI have been groundbreaking. Innovations like minimally invasive implantation techniques and high-resolution brain mapping have significantly enhanced the precision and safety of BCIs to date. Neuralink, among other projects, has garnered attention by developing ultra-high-density electrode arrays and wireless systems, pushing the boundaries of BCI capabilities.
However, they still present significant challenges to consider before neurotech BCIs can become a reality in modern society.
How to Make Brain-Computer Interface Technology More Accessible
Affordability: Cost remains a significant barrier to BCI accessibility. Of course, efforts to develop affordable BCI systems and components can democratize access. Still, chip production is minimal because its output costs fluctuate between hundreds to thousands of dollars per unit. Materials for production remain expensive, but to solve the issue, other materials like polymer materials are anticipated to help bring down the cost.
Scalability: Scalability is also essential — designing systems easily replicated or adapted for different purposes will broaden their reach. One concern is that the market for these devices isn’t big enough to sustain more in-depth research and development. However, its essential better interfaces help humans achieve a better understanding of the operational systems. Simplifying the interface of BCI systems and making them more user-friendly is pivotal. Open-source platforms encourage collaboration and innovation, allowing researchers and enthusiasts worldwide to contribute to BCI development. DIY kits and accessible software can facilitate learning and experimentation to improve the quality of the BCI interface and allow the market to expand, allowing us to understand the system better in preparation for complete scalability.
Community Engagement and Education: Initiatives that engage communities and promote education about BCI technology are crucial. Workshops, educational programs, and online resources can familiarize individuals with the concepts behind BCIs, fostering interest and participation.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations: Addressing ethical and regulatory concerns surrounding BCI technology is vital. In an age of cybersecurity risks, privacy and security will be one of the most prominent issues to resolve before entering the market. A cybersecurity system that is continuously upgraded and reviewed for errors is vital for BCIs to feel safe to the public, overriding the idea that a hacker could make its way into controlling someone through their own BCI. There are, of course, a myriad of other ethical issues to explore, including in the areas of justice, autonomy, and humanity/personhood. User safety and risk benefits are essential to honest patient conversations before utilizing these devices. Ensuring user privacy, consent, and security through clear regulations and ethical guidelines is necessary for widespread acceptance and trust.
As BCI technology continues to evolve, its accessibility remains a key focus. The amalgamation of innovation, accessibility, and ethical considerations will determine its widespread adoption. Collaborative efforts across disciplines are essential for making BCIs a part of our daily lives. With the hopes of improving lives, it is the quest of the innovators to help meet the ethical and technical standards for these devices. Further, while affordability will at first be a barrier to implementing these devices in more people, eventually, the demand in the BCI market may very well lead to expanding players and lowering costs as we develop new ways to improve upon the technology.